Are you frustrated with clogged pores after applying sunscreen? Wondering why that seemingly protective layer can turn into a skin nightmare?
Let’s uncover the mystery behind this skincare conundrum. The answer lies in understanding the intricate relationship between sunscreen and our pores.
By delving into the science of sunscreen formulation and its interaction with the skin, we can empower ourselves to make informed choices for more precise, healthier skin.
In this blog post, I will explore factors contributing to pore clogging and address common misconceptions surrounding sunscreen.
Get ready to unlock the secrets and discover the path to pore-friendly sun protection.
Why does sunscreen clog my pores?
I have explored three main reasons for this phenomenon:
- Some sunscreens have thick consistencies and contain emollients that can create a barrier on the skin, preventing it from breathing correctly and potentially leading to pore congestion.
- Certain sunscreen ingredients (such as certain oils or waxes) can likely clog pores and form comedones.
- Failure to properly cleanse and remove sunscreen residue from the skin can leave remnants that may accumulate and block pores over time, especially if combined with other factors like sweat or excess sebum production.
Not all sunscreens will clog pores for everyone.
We react differently to specific sunscreen formulations, and factors such as skin type, genetics, and individual ingredient tolerance can also play a role.
Exploring different sunscreen options, particularly non-comedogenic and lightweight formulations, is recommended to find one that works well for your skin without clogging your pores.
Let’s get deeper into this.
Exploring the rationale behind the use of sunscreen.
To see how sunscreen relates to pores, it is good to know the main characteristics of this type of product.
Sunscreens contain a variety of active and inactive ingredients. These are responsible for absorbing or reflecting UV radiation.
Common active ingredients include zinc oxide, titanium dioxide, avobenzone, oxybenzone, and octinoxate.
The inactive ingredients provide texture, stability, and additional benefits to the sunscreen formulation. They can include emollients, preservatives, fragrances, and other additives.

There are two different types of sunscreen. The physical sunscreens (you can also meet them as mineral ones) contain active ingredients like zinc oxide or titanium dioxide.
They work by sitting on the skin’s surface and reflecting or scattering UV rays. They are often well-tolerated by sensitive skin types and provide broad-spectrum protection.
Conversely, chemical sunscreens contain organic compounds like avobenzone, oxybenzone, or octinoxate.
They absorb UV radiation, convert it into heat, and release it from the skin. Chemical sunscreens are lightweight and easier to spread and blend into the skin.
Sunscreens form a protective barrier that either reflects or absorbs UV radiation, reducing its impact on the skin. You have to do it regularly and properly.
After covering the sunscreen topic, let’s see what happens with the pores.
How do pores function?
Pores are the pathway for sebum, sweat, and dead skin cells to reach the skin’s surface. They are small openings of hair follicles on the skin connected to sebaceous glands.
Sebaceous glands produce sebum, an oily substance that helps lubricate and protect the skin.
Pores play a crucial role in maintaining overall skin health. They help regulate the skin’s oil production by allowing sebum to reach the surface, moisturizing the skin.
Pores also aid in eliminating sweat and toxins from the body, promoting detoxification.
They assist in thermoregulating the body by allowing sweat to evaporate, helping to cool down the skin.
There are a couple of factors influencing pore size and appearance.
- Some of us may genetically have larger pores.
- Pores appear larger and more visible with age due to decreased collagen and elastin, reducing skin elasticity.
- Excessive sebum production can contribute to enlarged and more noticeable pores.
- Prolonged sun exposure can damage collagen and elastin fibers, decreasing skin elasticity and enlarging pores.
- People with oily or combination skin types often have more prominent pores than dry or normal skin.
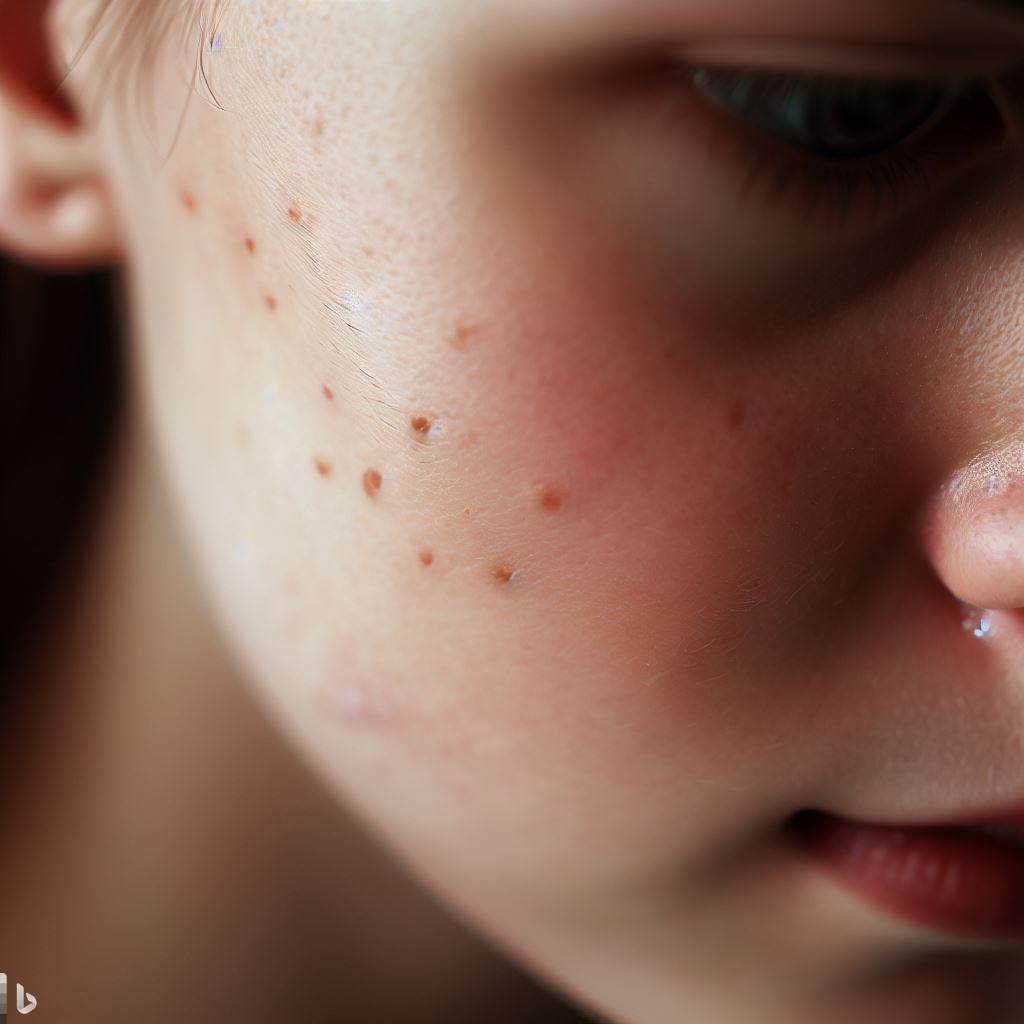
- When pores become clogged with excess sebum, dead skin cells, and debris, they can appear more prominent and give the skin a textured or congested appearance.
Now, let’s see how sunscreen interacts with pores.
Why would sunscreen clog pores?
Let’s dissect three probable reasons. The first is connected with heavy or occlusive formulations:
As mentioned, some sunscreens have thicker or heavier consistencies, which can create a barrier on the skin’s surface. These formulations may not allow the skin to breathe correctly, potentially leading to pore congestion.
Occlusive ingredients like certain oils, waxes, or silicones can contribute to the heaviness of the sunscreen and further clog pores.
The second reason might be related to comedogenic ingredients. Certain ingredients can clog pores and cause acne breakouts.
They are often defined as comedogenic and can vary from person to person regarding their pore-clogging potential. Common comedogenic ingredients in sunscreens include certain oils, fragrances, and thickening agents.
The third reason has something to do with Inadequate cleansing and removal. Failing to cleanse and remove sunscreen leaves a residue that may accumulate and clog pores over time.
Sunscreen that is not thoroughly removed can mix with sweat, sebum, and other impurities on the skin, exacerbating pore congestion.
Improper cleansing or using ineffective products to remove sunscreen can contribute to the issue.
What about if you have acne-prone skin? Let’s see.
How to pick up the right sunscreen for acne-prone skin?
Look for sunscreens labeled “non-comedogenic” or “won’t clog pores.”
Ensure your sunscreen offers sufficient sun protection by checking its Sun Protection Factor (SPF) rating.
Look for a minimum SPF of 30 or higher to protect against UVA and UVB rays adequately.
Consider choosing oil-free or oil-controlling sunscreens if you have oily or combination skin, as they can help control shine and minimize the risk of pore congestion.
It’s essential to consider your specific skin needs and preferences when selecting a sunscreen for acne-prone skin.
As everyone’s skin is unique, so what works for one person may not work for another.
Conduct patch tests, read product reviews, and consult with dermatologists or skincare experts for personalized recommendations.
Tips to prevent pore clogging
Ensure you thoroughly cleanse your skin to remove sunscreen residue at the end of the day. Use a gentle cleanser suitable for your skin type to avoid stripping the skin of its natural oils.
Pay attention to areas where sunscreen accumulates, such as the forehead, nose, and chin. Exfoliate your skin to remove dead skin cells, debris, and excess sebum that can contribute to clogged pores.
Choose gentle exfoliation methods suitable for your skin, such as chemical exfoliants containing AHAs (alpha hydroxy acids) or BHAs (beta hydroxy acids).

Exfoliate 1-2 times a week to avoid over-exfoliation, which can irritate the skin and potentially lead to more breakouts.
Explore sunscreen alternatives such as sun-protective clothing (e.g., wide-brimmed hats, long sleeves) and seek shade during peak sun hours to minimize sun exposure.
How to properly apply sunscreen to minimize pore clogging?
Instead of applying a thick layer of sunscreen, consider using multiple thin layers. Use a small amount of sunscreen on your fingertips and gently spread it over your skin, focusing on areas prone to sun exposure.
Give your skin enough time to absorb the sunscreen before applying makeup or other skincare products. This allows the sunscreen to form a protective barrier on the skin, reducing the chance of it mixing with other products and potentially clogging pores.
Follow the instructions on the sunscreen label regarding the recommended absorption time before proceeding with other products.
Use blotting papers or oil-absorbing sheets throughout the day to remove excess oil without disturbing the sunscreen layer.
Conclusion
Understanding why sunscreen can clog pores is crucial for maintaining healthy, blemish-free skin while enjoying sun protection’s benefits.
I’ve explored factors contributing to pore cloggings, such as heavy formulations and comedogenic ingredients.
You can minimize the risk of clogged pores and breakouts by following tips like applying sunscreen in thin layers, allowing proper absorption time, and incorporating blotting techniques.
Finding the right sunscreen that suits your skin and consistently practicing proper skincare habits will help you achieve a beautiful, protected complexion.
Embrace the power of sunscreen without compromising your skin’s health and vitality.
Thank you for reading!
Valeria







